Kotlin基础篇(一)
Kotlin基础篇(一)
#1:变量
kotlin的变量定义有两种**val**和**var**。
第一种**val**
```
val i=10;
```
val定义的变量为不可改变量,如上面i=10后,如果我们添加
```
i+=10
```
首先编译器(android studio)就会提示我们报错!
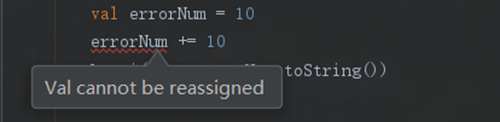
错误信息是:**Val cannot be reassigned**
第二种 **var**
```
var num = 10
num += 10
```
#2:函数
```
fun addSum(i1: Int, i2: Int): Int {
return i1 + i2
}
```
看下上面的代码,我们简单分析下组成
```
fun函数定义关键字;
addSum函数名;
i1:Int对应参数名以及参数类型,中间用:分隔;
也就是说函数中变量的使用方式是name: type的格式,
当然我们还是给参数指定默认值,
怎么去写呢?
很简单,
fun addSum2(i1: Int=0, i2: Int=1): Int {
return i1 + i2
}
这么我们使用的时候就可以这么写:
Log.i(tag, addSum2(num).toString())
两个参数后面的: Int则代表函数的返回值类型;
```
kotlin里面Int是首字母大写,与java中int类似,但是java里面的int是基本类型,而kotlin里面则是一个类。简单截个Int的代码:
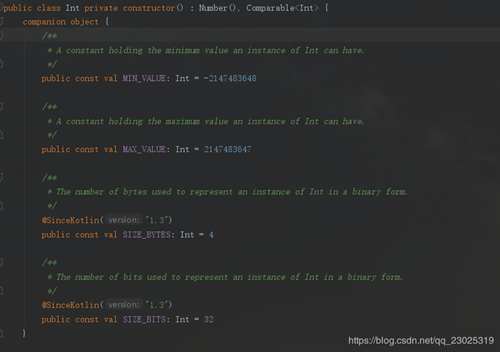
kotlin中还可以把上面的函数更简化:
```
private fun addSum2(i1: Int, i2: Int = 2): Int = i1 + i2
```
可以看到当函数返回单个表达式的时候,我们可以吧{}以及return等省略,替换为=,等号后面就是指定的代码体。
参数默认值的写法有人会发现,我的传个Int 和string,怎么报错了?
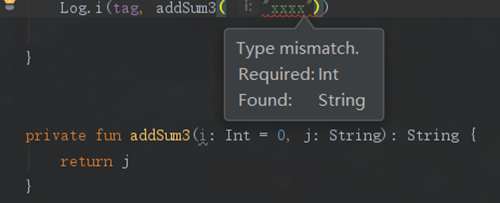
那么像这种我们怎么传值呢?kotlin当然考虑到了这个问题,而且给出了新的用法,键值对传值的方法:
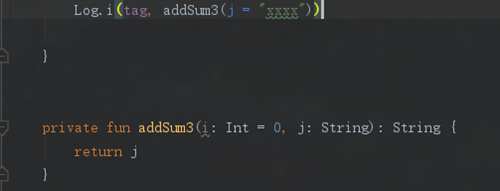
如图所示,我们制定参数名称就可以,是不是很方便?
#3:集合
首先来张整体的框架图:
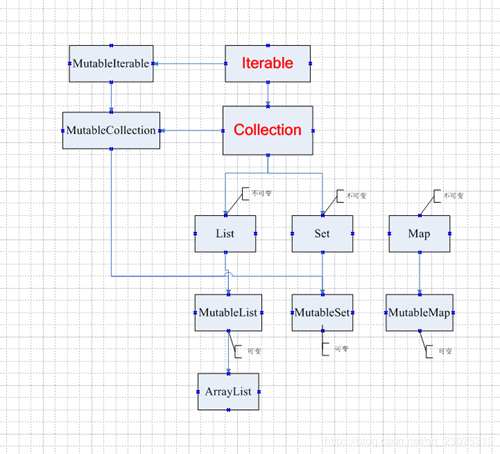
可以看到顶层的四个基本接口分别是:
**Iterable**,**MutableIterable**,**Collection**,**MutableCollection**。
而下面六个在创建的时候又分为**可变和不可变集合**。
##3.1 list
首先,我们来看下list相关:
构建list,我们需要用到标准的库函数listOf(),listOfNotNull(),mutableListOf(),arrayListOf(),其中前两个是不可变集合,后两个是可变的。
```
val list1 = listOf(1, 2, 3)
val list2 = mutableListOf(1, 2, 3)
val list3 = arrayListOf(2, 3, 4)
val list4 = listOfNotNull(1, 3, 4)
```
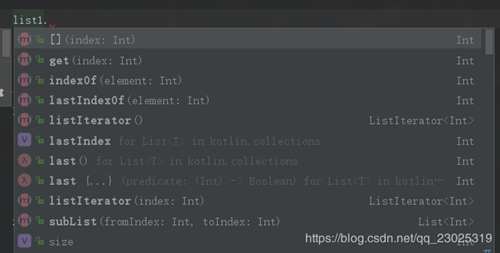
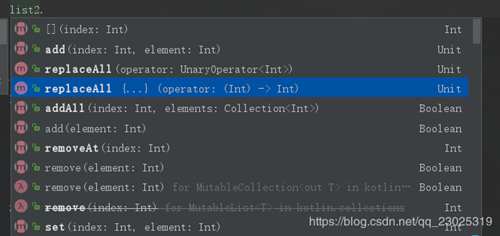
可以看到构建集合是非常简单的,而且mutableListof构建的list2中有add,remove等方法,也就是可变集合。
至于listOfNotNull我们打印下看下输出结果:
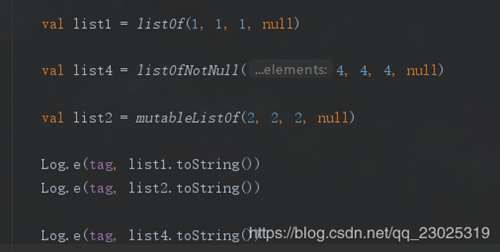
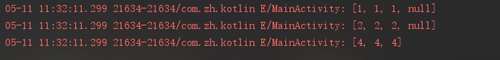
可以看到 listOfNotNull自动将null忽略,可以看下源码:
```
/**
* Appends all elements that are not `null` to the given [destination].
*/
public fun C : MutableCollectionin T, T : Any Arrayout T?.filterNotNullTo(destination: C): C {
for (element in this) if (element != null) destination.add(element)
return destination
}
```
可以看到,在底层如果参数为null就不会添加到destination中。
到这里,构建list已经完结,我们来接着看遍历list:
这里我们先说下kotlin中的循环遍历分为两种,for循环和while循环。
```
val list1 = listOf(1, 1, 1, null)
for (i in list1) {
println(i)
}
var size = list1.size - 1
while (size = 0) {
println(list1[size])
size--
}
```
另外除了这两种外,我们还可以使用Lambdas表达式,
```
list1.forEach { println( it) }
```
这种是不是更方便?
##3.2 set
set构建主要有setOf(),mutableSetOf(),hashSetOf(),linkedSetOf();
```
val set1 = setOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 21)
val set2 = mutableSetOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 21)
val set3 = hashSetOf(1, 2, 3)
val set4 = linkedSetOfInt(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
```
其中只有setOf()是只读,其余都是可读写的。
包含add,addall,remove等方法。
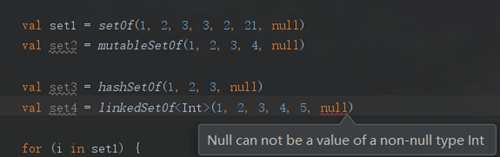
另外从上图可以看出,linkedSetOf()是不允许有null值的。
其次,set中会自动去除相同元素,这点跟java是一致的。
比如set1中,虽然我们赋值了7个值,但是set1实际为[1,2,3,21,null].
##3.3 Map
MapK, out V 是以键值对的形式存在,与list,set一样,构建时都分为可变和不可变集合。
其中mapof()为不可变;
而linkedMapOf(), hashMapOf(),mutableMapOf()是可读写的。
```
val map1 = mapOf(1 to map1-1, 2 to map1-2, null to null)
val map2 = linkedMapOf(1 to map2-1, 2 to map2-2, null to null)
val map3 = hashMapOf(1 to map3-1, 2 to map3-2, null to null)
val map4 = mutableMapOf(1 to map4-1, 2 to map4-2, null to null)
println(map1--------------------------)
map1.forEach { (key, value) - println($key t $value) }
println(map2--------------------------)
map2[3] = map2-3
map2.forEach { (key, value) - println($key t $value) }
println(map3--------------------------)
map3[3] = map3-3
map3.forEach { (key, value) - println($key t $value) }
println(map4--------------------------)
map4[4] = map4-3
map4.forEach { (key, value) - println($key t $value) }
```
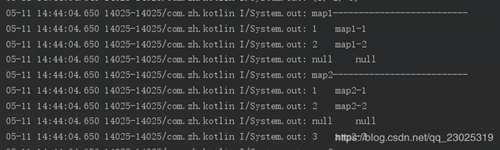
可以看到输出结果,map的键值对是可以为null的。
#4:数组
kotlin中数组是Array;代码很简单,我们直接上代码:
```
public class ArrayT {
public inline constructor(size: Int, init: (Int) - T)
public operator fun get(index: Int): T
public operator fun set(index: Int, value: T): Unit
public val size: Int
public operator fun iterator(): IteratorT
}
```
可以看到,get和set方法,以及遍历和长度。
首先我们根据constructor来创建数组
```
var array0 = Array(3) { i - i + 1 }
```
其中3是指数组长度size;i-i+1赋值。
另外一种则跟list,set等一致,使用arrayOf();
```
val array = arrayOf(1, 2, 3)
array[1] = 100
array.forEach { println(it) }
```
# 5:数组,集合转换
## 5.1数组转集合
```
val array = arrayOf(1, 2, 3)
```
数组创建好了,开始转,这里用到的是toList方法。
```
/**
* Returns a [List] containing all elements.
*/
public fun T Arrayout T.toList(): ListT {
return when (size) {
0 - emptyList()
1 - listOf(this[0])
else - this.toMutableList()
}
}
```
逻辑很简单,如果size为0,则返回空集合,
如果为1,则使用listof()创建不可变集合;
否则使用toMutableList();
```
/**
* Returns a [MutableList] filled with all elements of this array.
*/
public fun T Arrayout T.toMutableList(): MutableListT {
return ArrayList(this.asCollection())
}
```
也很简单,返回ArrayList。
当然,Array转换的方法不止toList一种,
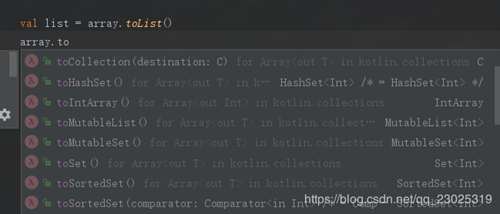
感兴趣的朋友可以每个都熟悉下。
## 5.2集合转数组
这里拿toIntArray为例:
```
/**
* Returns an array of Int containing all of the elements of this collection.
*/
public fun CollectionInt.toIntArray(): IntArray {
val result = IntArray(size)
var index = 0
for (element in this)
result[index++] = element
return result
}
```
代码很简单1:构建Int数组 2:for赋值 3:返回array。
另一种则是:
```
val listStr = listOf(list, set, map)
val arrayStr = listStr.toTypedArray()
arrayStr.forEach { println(it) }
```
以上就是(Kotlin基础篇(一))全部内容,收藏起来下次访问不迷路!